The content of the site is protected by copyright as intellectual property. Without the written consent of romehome.ro, copying (in any form) of any part of the website (design, text, images, etc.) is not accepted.
„God is in the details” – Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
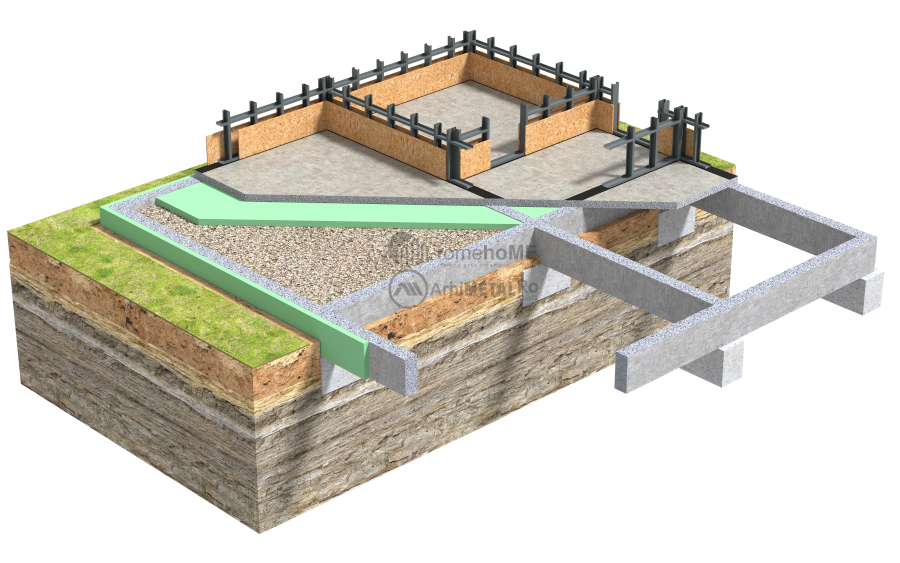
Foundations
One of the major advantages of frame constructions is that they are lightweight, resulting in foundations that are up to 40% smaller compared to traditional masonry and reinforced concrete foundations.
TYPE OF FOUNDATIONS
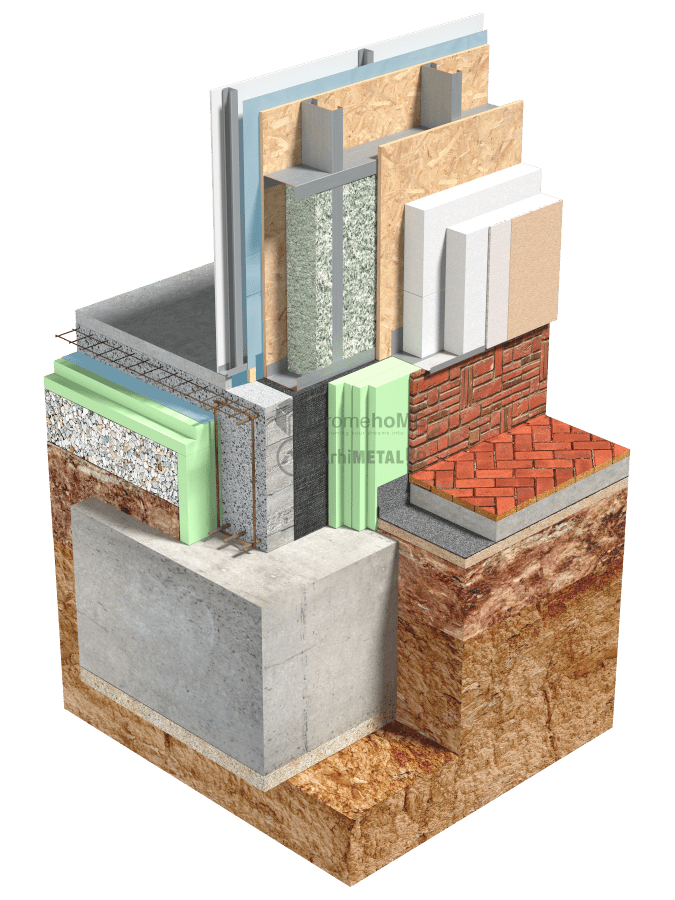
Foundations on Blocks and Foundation Beams
This is the usual solution for constructing foundations for frame structures made of thin-walled galvanized steel profiles. The foundation beams have approximate dimensions of 0.25 x 0.75m (length x height) and are supported by foundation blocks with a depth of 0.8 – 0.9m. The dimensions of the blocks and foundation beams are calculated based on the terrain, the shape and size of the house, and the arrangement of the frame walls.
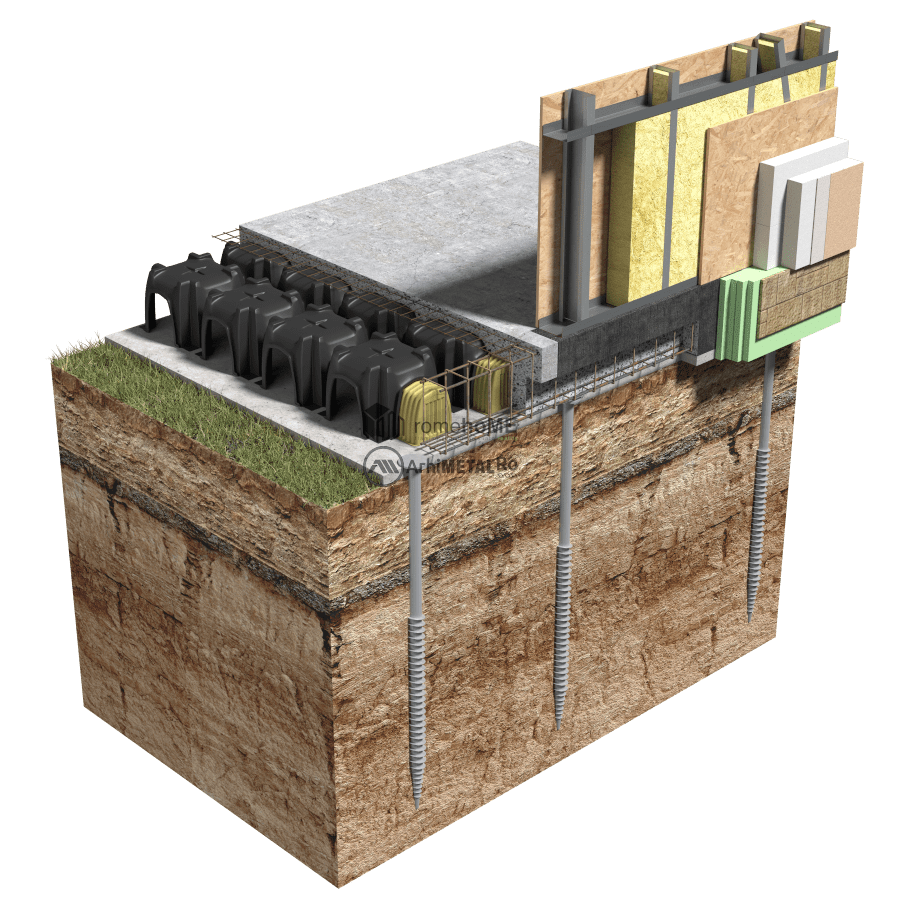

Foundations on Drilling Piles with Aerated Rigid Plate
Due to the lightweight nature of the frame structural system (40 – 60kg/m²), screw-in micro-piles can be used as an alternative to traditional concrete foundations. This not only reduces construction time but also has a minimal environmental impact, allows for foundation on all types of terrain, and offers a comparable cost to reinforced concrete foundations for a conventionally built structure.
Depending on project requirements and the nature of the foundation soil, other foundation solutions can also be used (such as a raft foundation).
In all cases, the surface of the concrete slab on which the frame structure will be installed should not have unevenness or level differences greater than 5mm!
WATERPROOFING OF FOUNDATIONS
Protection against meteoric water (rain, snow, etc.) and water from soil capillarity is an important requirement that we take very seriously.
To break the soil capillarity, a layer of gravel (Ø24-32) with a minimum thickness of 20 cm is recommended, or according to the detail in the technical project (TP).
A strip of waterproofing membrane with a width of 20 cm is placed beneath the path of the frame walls.
On the sides of the foundation beams, waterproofing membrane can be used either as an extension of the one beneath the walls or as waterproof paint.
In the case of older foundations where the detailed composition is unknown, for enhanced waterproofing, a waterproofing membrane can be installed over the entire surface of the concrete slab.
THERMAL INSULATION OF FOUNDATIONS
Thermal insulation of foundations is a necessary (and obligatory!) element to prevent the influence of external factors from affecting the interior of the structure and altering its microclimate.
Extruded polystyrene (XPS) is used as the thermal insulation material, on top of which a polyethylene (PE) film is applied to prevent cement milk from seeping between the polystyrene sheets and to provide protection against moisture from soil capillarity.
As a general rule, the thickness of the thermal insulation is calculated for each individual construction, but a minimum thickness of 10 cm of extruded polystyrene (XPS) below the concrete slab and a minimum thickness of 10 cm on the exterior of the foundation beam is a starting point.
ACCESS POINTS
The design of entrances/exits should consider the dimensions of the openings and the arrangement of the windows and doors (within the thermal insulation or on the face of the wall).
To prevent thermal bridges at the foundation and at the floor level at +/- 0.00 elevation, access points from ground level (stairs, terraces, platforms, etc.) require additional thermal insulation. This condition is mandatory for energy-efficient constructions.
PROTECTION OF FOUNDATIONS
This primarily refers to mechanical protection against the roots of trees planted near the construction. Regardless of the type of foundation, whether concrete or micro-piles, large-crowned trees should be planted at a minimum distance of 6-9 m depending on the species, or a minimum of 3 m for small to medium-sized shrubs.
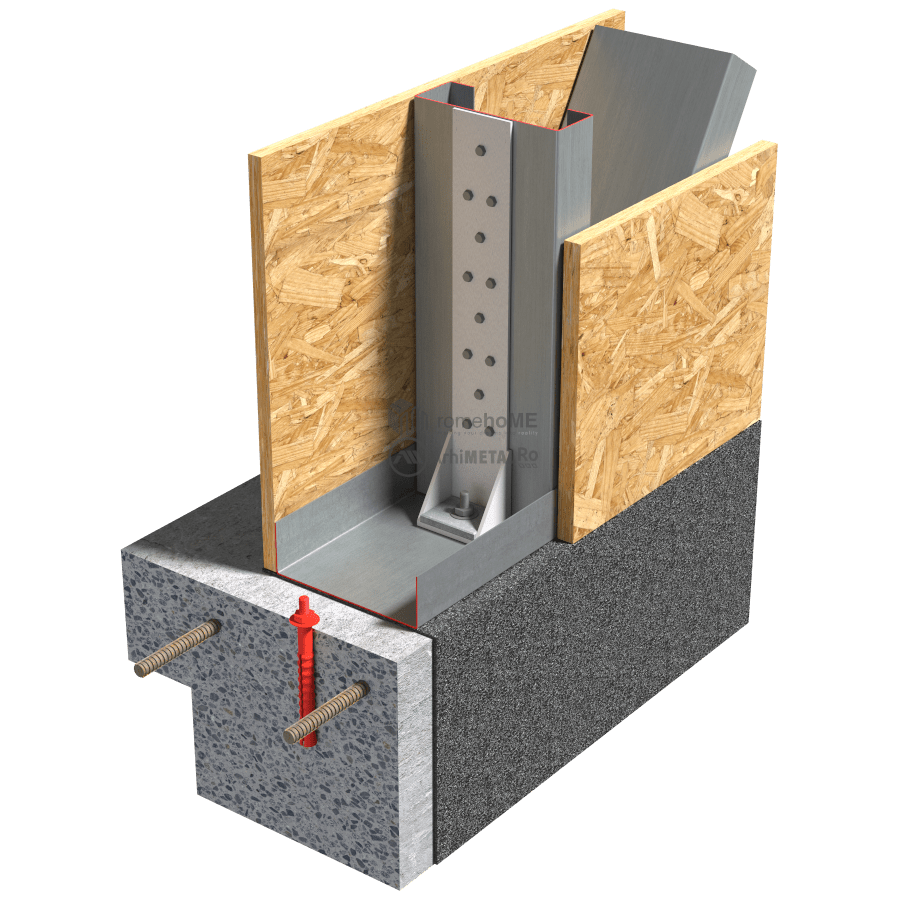
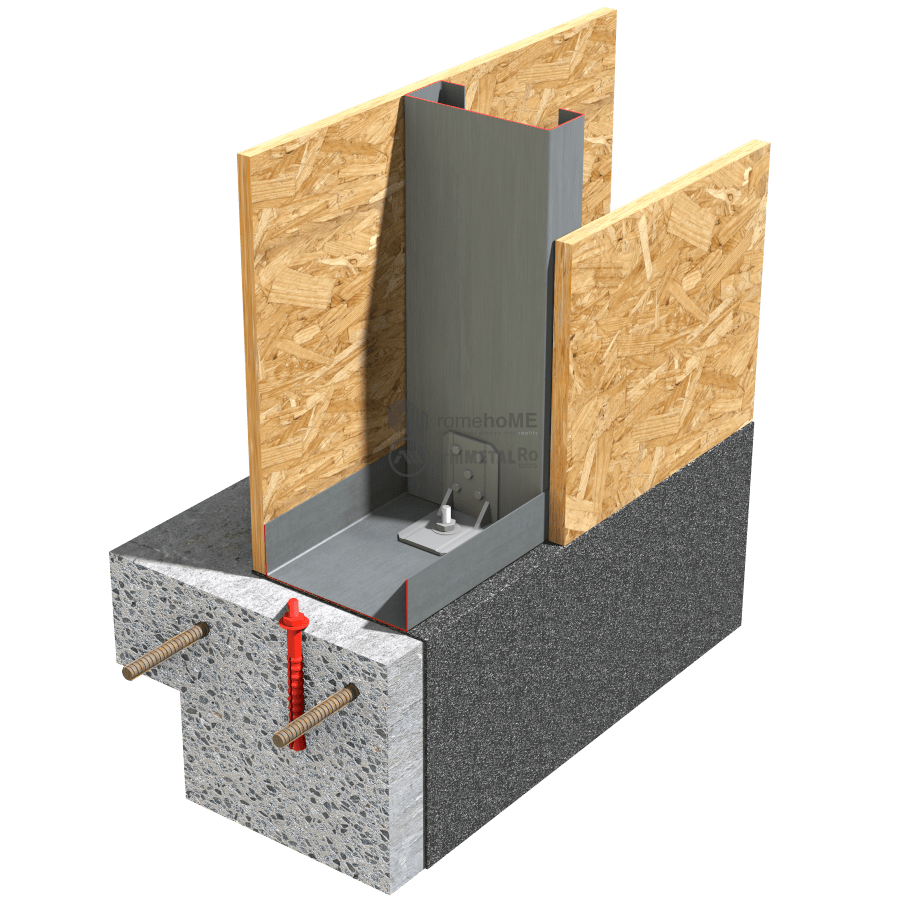
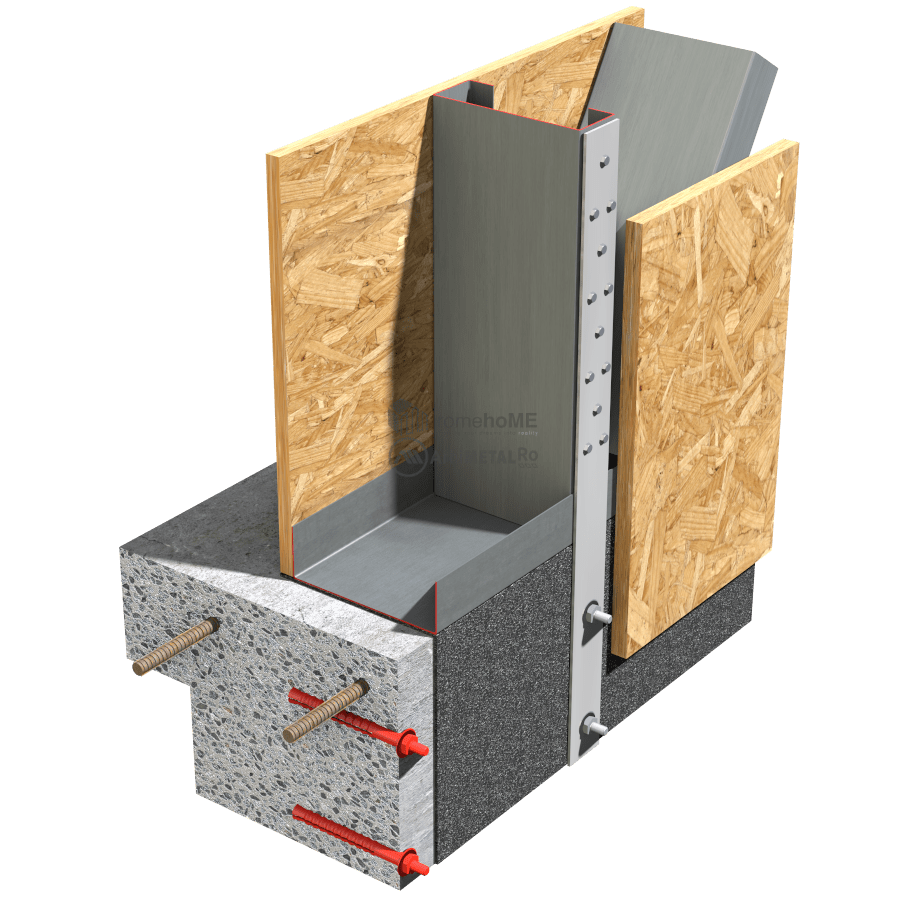
DETAILS OF ATTACHING FRAME WALLS TO FOUNDATIONS
An important condition for the proper functioning of the frame structure regardless of the applied forces is for the studs (C-shaped profiles) to be directly fixed to the foundation.
Simply attaching the U-profile to the concrete slab is not sufficient. Generally, the method and type of fixation are chosen by the structural engineer based on calculations and project requirements.
Concrete fixation is done with chemical or mechanical anchors (M14-16), and corner brackets or galvanized steel straps are used for fixing the profiles. It is recommended to maintain a greater installation distance from the edge of the reinforced concrete slab (80-100mm). This minimizes the possibility of concrete cracking at the edges or around the reinforcement when drilling holes for anchor fixation.