The content of the site is protected by copyright as intellectual property. Without the written consent of romehome.ro, copying (in any form) of any part of the website (design, text, images, etc.) is not accepted.
„God is in the details” – Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
Intermediate floors and stairs
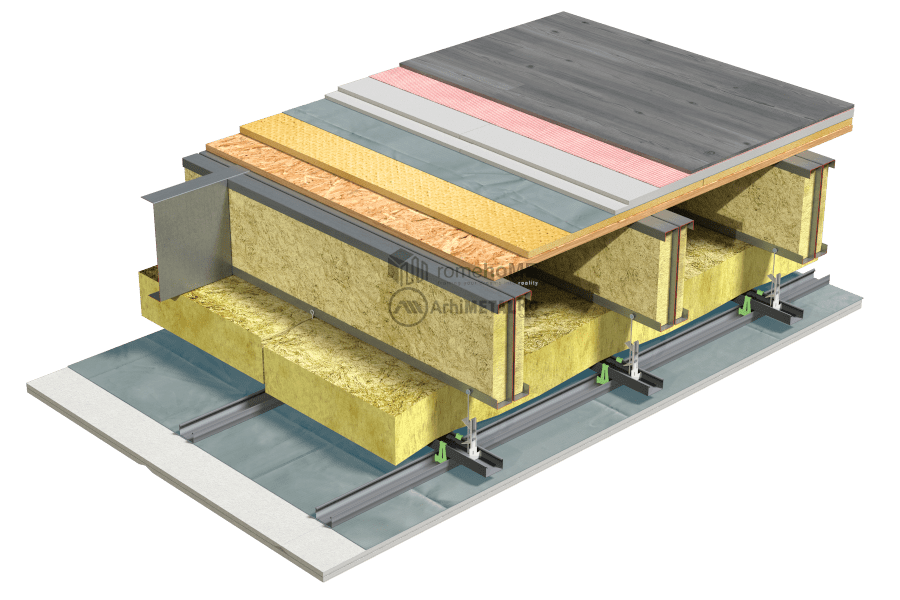
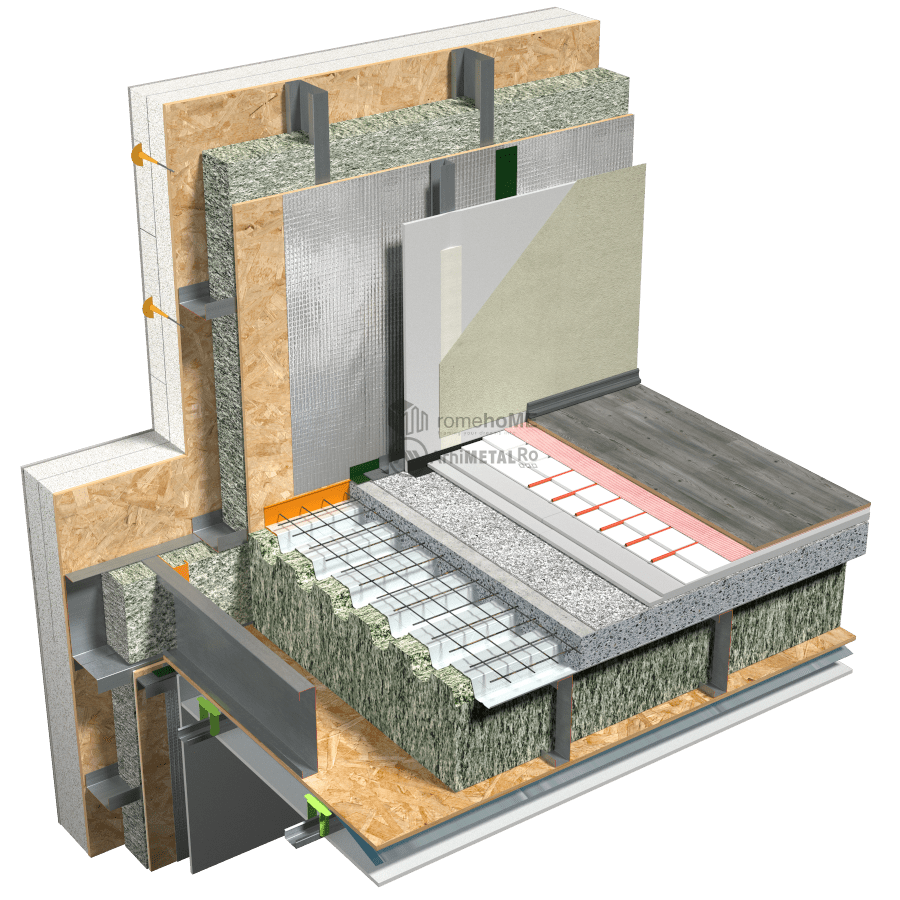
The composition of intermediate floors can respond to multiple types of requirements (structural, acoustic, thermal insulation, etc.) based on the specific project needs.
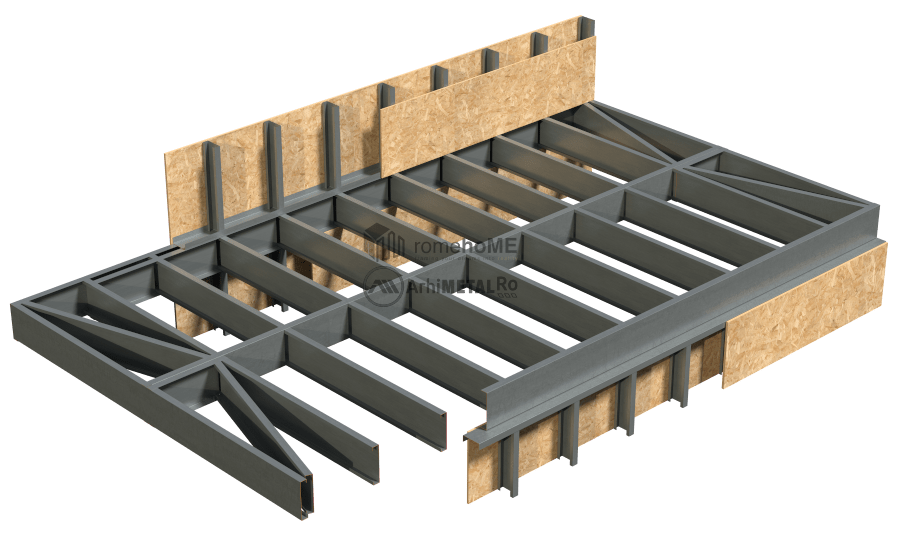
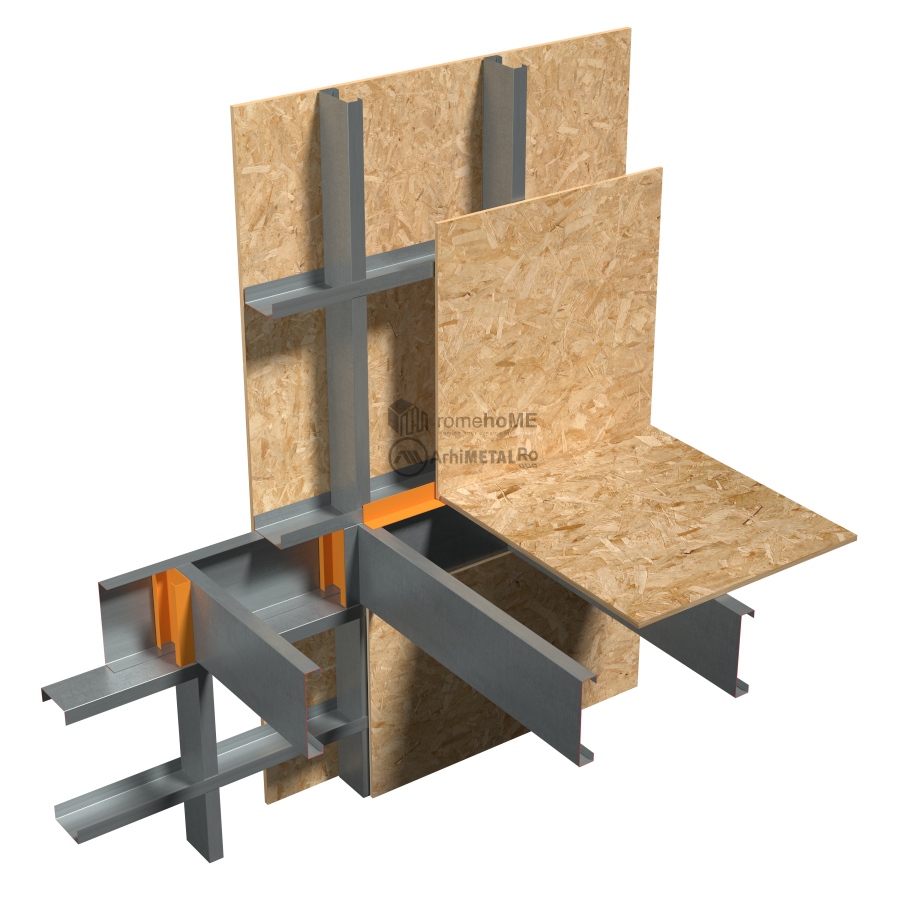
FRAME STRUCTURE
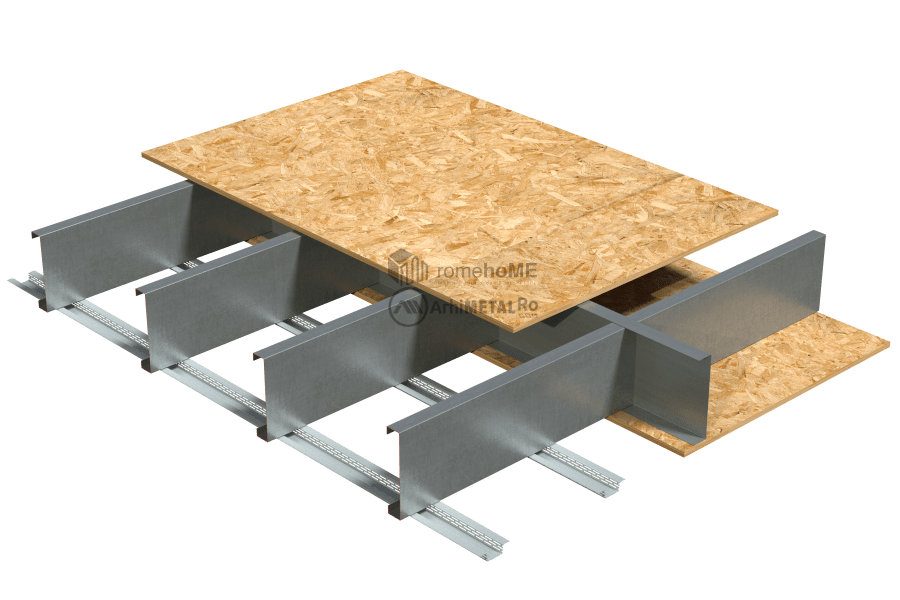
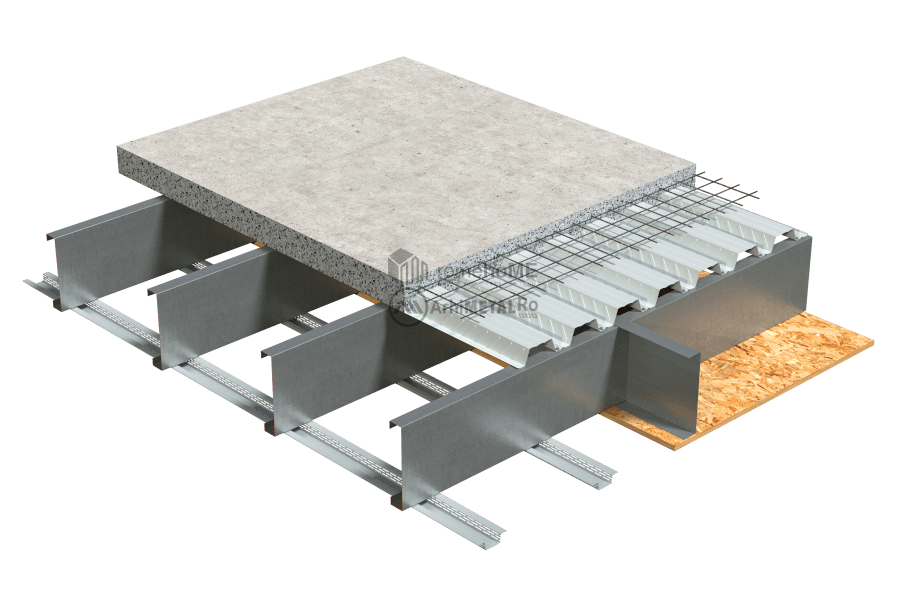
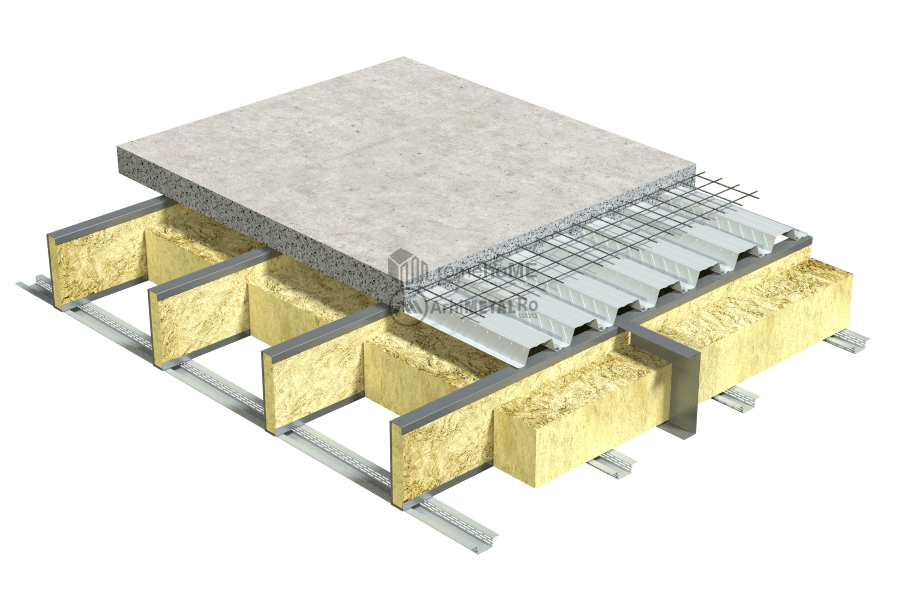
C/U200 or C/U300 profiles with single or double arrangement (back-to-back) depending on the loads and project requirements.
There are two ways to arrange the floor within the frame structure:
• with interrupted wall studs by the floor;
• with continuous wall studs.
For stairs, there are various options for designing the steps, including the width of the ramp, the method of fixation to the side walls, and the desired final appearance.
When determining the height of the risers, it is crucial to specify the floor layers at the starting and ending points, including any intermediate platforms, to ensure structural calculations and ramp modeling prevent any discrepancies in the first and last steps.
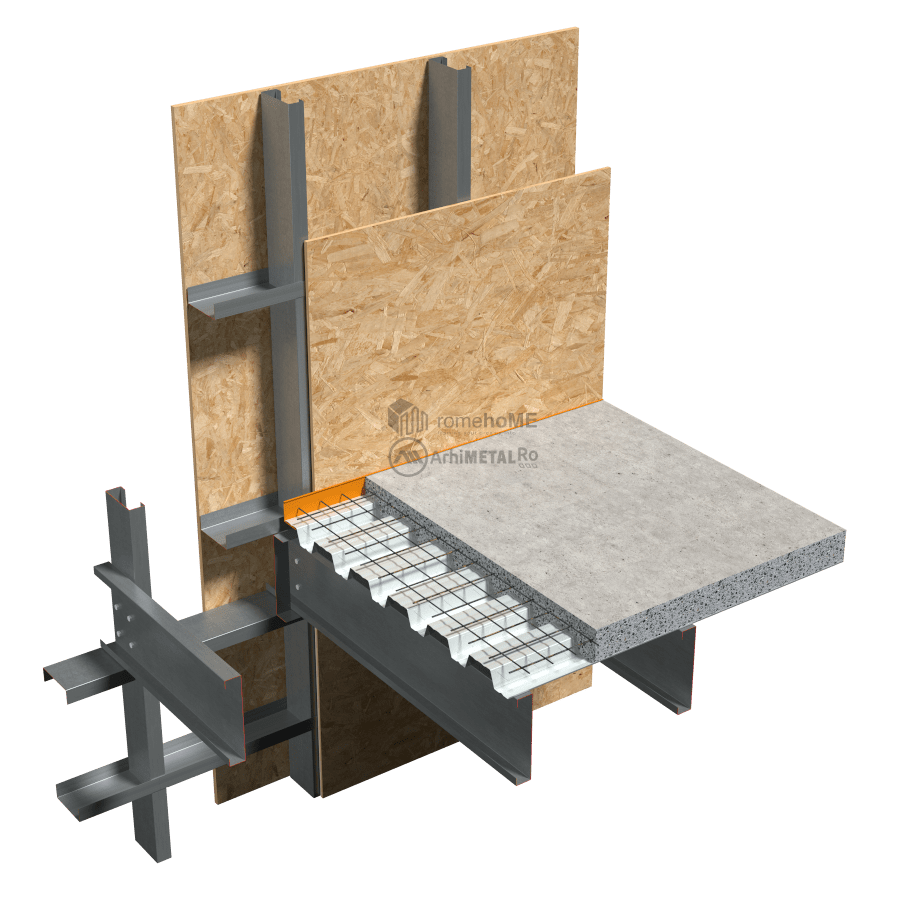
FLOORING OF THE FLOOR
There are two options for the upper part of the floor:
• flooring with 22 mm thick OSB 3, either in one or even two staggered layers, or replacing the second layer of OSB with a cement-based board based on specific flooring requirements;
• using a poured concrete floor in a permanent corrugated sheeting formwork;
Depending on the insulation used – mineral wool, cellulose fibers, wood fibers – at the lower part of the frame structure, either only profiles for fixing gypsum boards can be used, or it can be closed with a 15 mm thick OSB 3 board to which the support structure for the gypsum boards can be attached.
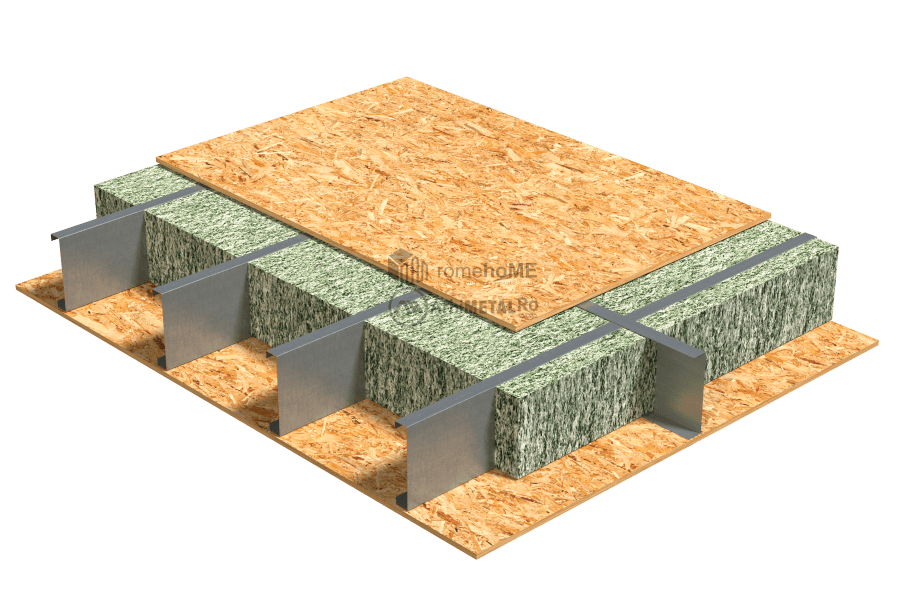
INSULATION
Within the frame structure
For insulation inside the steel structure, we recommend two product options:
- thermal insulation made of cellulose fibers, wood fibers, or mineral fibers;
These are inserted under pressure into the gaps between the profiles and require the cladding with OSB on both sides of the frame structure or OSB on the lower side and a concrete board on the upper side. This type of insulation ensures a uniform distribution of the insulation material in the interior cavities of the floor.
- thermal insulation made of mineral wool;
Similar to walls, mineral wool should be installed inside the C profiles before being placed in the gaps between the profiles. The use of mineral wool does not require OSB cladding on the lower side of the structure.
Both options contribute to both thermal and acoustic insulation of the rooms.
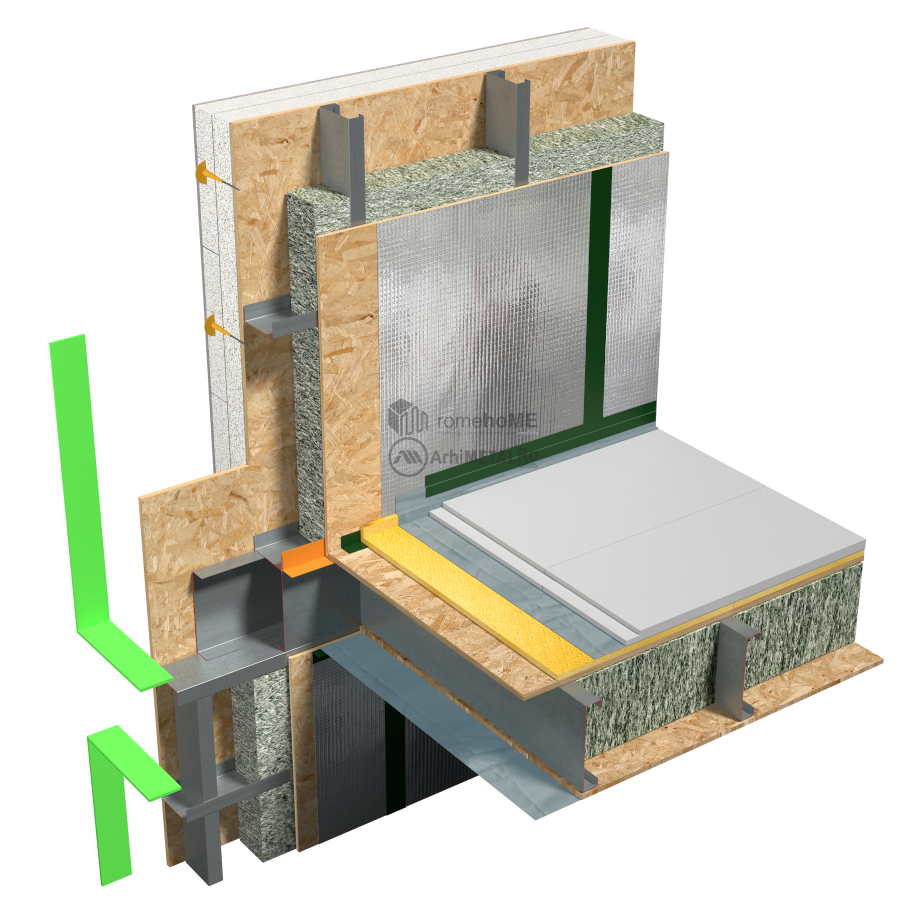
SEALING
Just like with walls, sealing the intermediate floors is a mandatory requirement for the proper functioning of the construction
There are several approaches:
• sealing both the upper and lower parts of the floor, with each room becoming a separate cell where humidity and temperature can be controlled without issues – an efficient solution recommended especially for residential constructions.
• sealing the upper part of the floor, with sealing around the floor beams on the lower part – this detail can be used for very large spaces (commercial, sports, manufacturing, etc.) where there are no significant variations in temperature or humidity.
It should be noted that rooms with high relative humidity, such as bathrooms and kitchens, need to be sealed correctly to achieve a construction with a healthy indoor microclimate.’

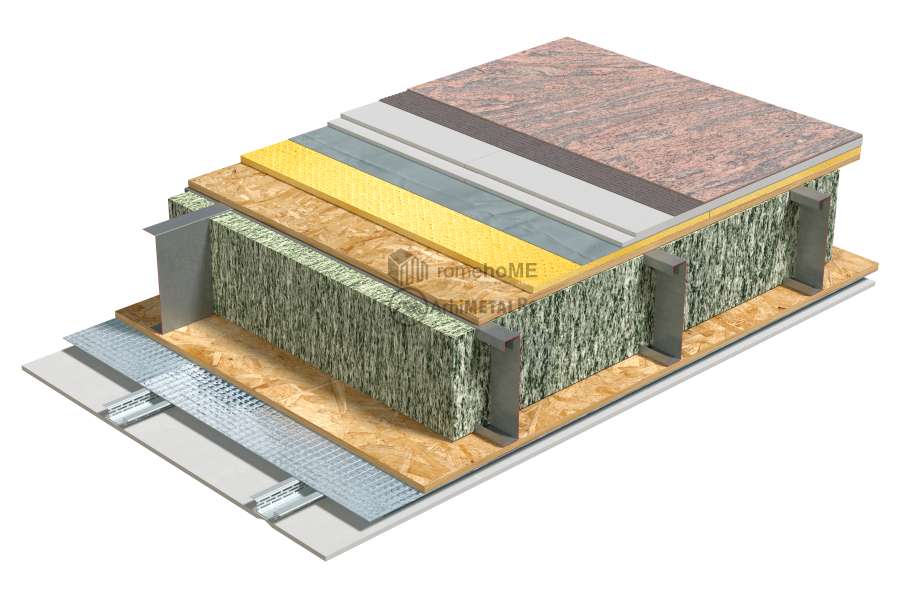
FLOORING AND STAIRCASE FINISHING
All types of finishes can be used!
It is extremely important to consider requirements related to impact noise, waterproofing, and underfloor heating.
As a floating layer (to reduce impact noise), rigid boards made of mineral wool, expanded or extruded polystyrene, or thin cork membranes or other aggregates can be used.
Dry screeds are used, easily accommodating low-profile underfloor heating systems with a height of 18mm.
In the case of bathrooms and/or kitchens, waterproofing of the floor and walls is done using cement-based waterproofing paints, reinforced at the junctions between walls and between walls and the floor.
TECHNICAL GAPS AND INSTALLATIONS
Similar to walls, installation routes and penetrations through the floors can be easily managed if specified during the design and 3D modeling phase.
PLASTERBOARD CEILING CLADDING
It is the simplest yet most effective method to enclose the underside of the floors.
Plasterboard panels can be installed on their own structure, fixed to the frame structure, or directly on the OSB board. This recommended detail allows for the installation of electrical or ventilation systems.
Depending on the project requirements, all recommended installation details from plasterboard system manufacturers can be used.